How Virtual Reality is Enhancing Training Quality in the Business Sector

In today’s fast-paced and technologically advanced world, businesses are constantly seeking innovative methods to train and upskill their workforce. Traditional training methods, such as seminars and online courses, often fall short due to limited engagement, inconsistent delivery, and high logistical costs. Virtual Reality (VR) is reshaping how companies approach employee development.
Virtual Reality offers immersive, interactive, and scalable training environments that replicate real-world scenarios without the associated risks. This article explores how VR is enhancing training quality in the business sector by improving employee performance, engagement, and knowledge retention. From sales and customer service to manufacturing and soft skills development, VR is making a measurable impact across industries.
Understanding VR in a Business Training Context
Virtual Reality is a computer-generated simulation that enables users to interact with a 3D environment through specialised equipment such as headsets and motion controllers. In business training, VR is often delivered through simulations that replicate real-life job scenarios, such as operating machinery or conducting a sales pitch. Role-playing scenarios help employees practice customer interactions or conflict resolution, while gamified learning modules boost motivation by using elements of game design. These formats allow for consistent content delivery, immediate feedback, and safe environments to practice and repeat complex tasks without real-world consequences. By catering to different learning styles and keeping users actively engaged, VR significantly enhances the overall effectiveness of corporate training.
Key Benefits of VR Training in Business
VR-based training offers numerous advantages across industries. First, immersive environments have been shown to significantly improve knowledge retention. VR fully engages learners by placing them in interactive, 3D environments that mimic real-world situations. This level of immersion helps anchor information more effectively than passive methods like reading or watching videos, and promotes long-term recall. In addition, learners retain more when they do rather than just listen. VR enables hands-on practice, allowing users to apply knowledge immediately, which reinforces memory through experiential learning.
Second, VR makes training highly engaging through interactive elements, increasing motivation and attention. Employees are more likely to stay focused and complete training when it involves visual and kinesthetic experiences. This sense of presence helps learners internalise content more deeply. Consistency and standardisation are also key benefits. Unlike in-person sessions that vary with instructors or locations, VR ensures every employee receives the same high-quality experience.
Another major advantage is the ability to practice in a risk-free environment. Employees can make mistakes without fear of real-world consequences, which is invaluable in high-risk sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics. Practicing emergency protocols, safety measures, or sensitive customer interactions in VR helps build muscle memory and emotional readiness.
Using VR for practical training is also a sustainable choice. Since environments and scenarios are digitally simulated, there is no need for consumables like fuel, raw materials, or other resources that traditional training often requires. This is especially relevant for machine operation, vehicle handling, and heavy equipment training, where fuel consumption and environmental impact are substantial. A clear example is flight simulation—aviation fuel is costly and has a significant ecological footprint, but VR eliminates the need for it. The same applies to vocational training more broadly. Fields like construction or catering typically involve high material use during instruction, but VR can dramatically reduce waste while still offering hands-on, realistic practice. Framing VR as an environmentally friendly solution also aligns well with sustainability goals such as the EU’s Green Deal, making it a compelling narrative for projects.

Furthermore, VR training often accelerates learning, enabling faster skill acquisition and improved confidence. Employees trained via VR report higher satisfaction, reduced anxiety when performing new tasks, and greater autonomy on the job. Faster on boarding translates into cost savings and increased productivity. VR places knowledge within a meaningful context. For example, instead of memorising steps from a manual, learners might perform them in a simulated factory floor or emergency room, helping them recall information when it’s most needed.
In terms of scalability, VR allows companies to deploy standardised training modules across various branches and geographical locations without the need for extensive travel or personnel deployment. This makes it ideal for multinational corporations and growing enterprises seeking uniformity in skill development. An additional advantage of VR lies in the frequency and efficiency of exercise repetition. Simulated processes can be reset almost instantaneously, enabling learners to attempt a given task multiple times within a short period. By contrast, preparing machinery or physical environments for repeated training exercises is often time-consuming and resource-intensive. This capacity for rapid repetition not only improves pedagogical efficiency but also further enhances the ecological benefits of VR-based training.
Virtual reality is emerging as a powerful tool for education because of its impact on both understanding and retention. In a study with 99 university students, Allcoat and von Mühlenen (2018) compared learning across three conditions: VR, traditional- textbook, and video. They found that students in the VR group performed significantly better at remembering content than those using textbooks or videos. When it came to understanding, VR learners performed on par with textbook learners and both outperformed video-based learners. Beyond test scores, the study also revealed that VR participants reported higher engagement and more positive emotional responses, suggesting that VR learning environments not only boost performance but also make the learning experience more enjoyable and motivating.
These benefits are supported by broader research showing that VR’s immersive and interactive qualities stimulate imagination and deeper engagement with material (Huang et al., 2010). Furthermore, its ability to provide embodied and multisensory learning helps learners retain knowledge more effectively and transfer skills to new contexts, while enhancing motivation and positive emotions (Johnson-Glenberg, 2018).
Lastly, VR systems often include real-time feedback, helping learners identify mistakes and correct them instantly—reinforcing correct behaviour and understanding.

Learning in immersive interactive environments for the Business Sector
Adaptability is essential in a constantly evolving workplace. With organisational structures becoming flatter and more agile, employees must learn to pivot between roles, adopt new technologies, and embrace innovation quickly. Creativity also plays a major role in differentiating businesses in saturated markets, making ideation and problem-solving important day-to-day assets.
Virtual reality (VR) enhances training quality by offering immersive, interactive environments where learners can practice these skills in lifelike scenarios. VR helps build and refine these skills through realistic simulations that provide hands-on practice and real-time feedback. For example, leadership development modules might simulate difficult performance review conversations or strategic meetings under pressure. Customer service scenarios challenge learners to balance professionalism with empathy in emotionally charged exchanges.
Public speaking modules place learners in front of a virtual audience with varying reactions and feedback, helping them manage anxiety and improve their delivery. Empathy training might simulate working with customers with disabilities, fostering inclusivity and perspective-taking.
MBSS Training Registry
In the context of immersive learning, the MBSS training registry contributes to enhancing training quality by providing a structured framework that directly connects employers with the offerings of training providers. Through differentiated profiles, the platform facilitates targeted functionality: employers gain tools to identify and engage with XR-based training that addresses specific organisational skill requirements, and can assign their employees to selected trainings, while providers can curate and present programs that respond to demonstrable market needs. This dual-structured system strengthens the alignment between training supply and demand, thereby supporting the development of a more adaptive, high-quality learning ecosystem within the business services sector.
You can find the registry page (which we created as part of our project activities) at the link below.
The Registry of Training Services
Case Studies and Real-World Success Stories
Numerous companies have already embraced VR training with notable results. Walmart, for instance, uses VR to train employees in customer service, compliance, and even crowd control during Black Friday events. With over a million associates trained using Oculus VR headsets, Walmart has reported reduced training time and improved staff confidence and customer satisfaction.
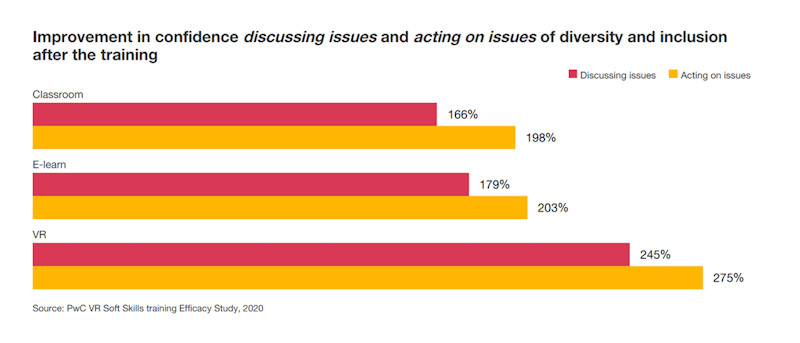
Firm PwC adopted VR to train staff on soft skills, including inclusive leadership and decision-making. A 2020 study by PwC found that employees trained with VR were four times faster to train than those trained via traditional e-learning and in the classroom and 275% more confident in applying their skills.
How specific industries are using VR training
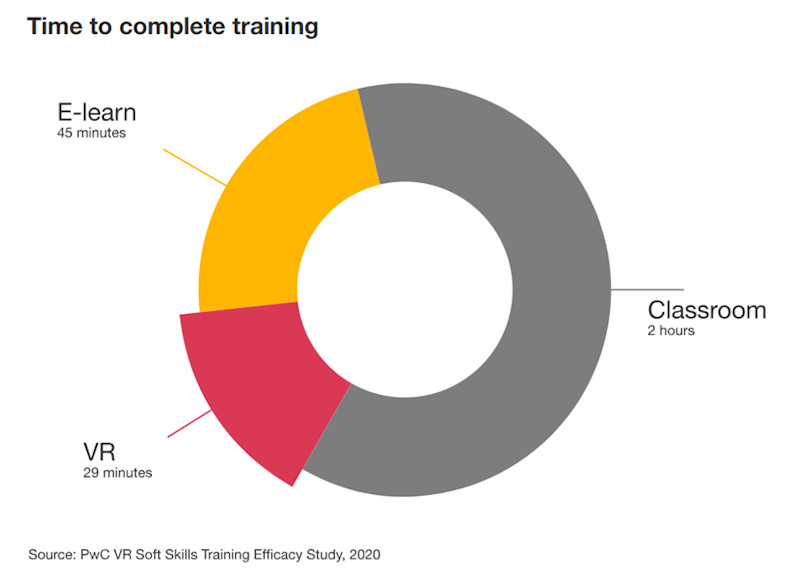
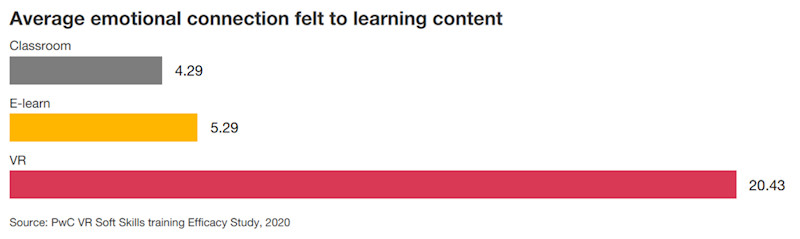
Several industries are already experiencing the impact of VR-based training. In retail, Walmart has rolled out VR modules to prepare employees for real-world scenarios such as Black Friday crowds or handling irate customers. These simulations allow staff to practice upselling, conflict resolution, and store management in a safe environment. Results have been impressive: Walmart reported a 30% boost in customer satisfaction, 10–15% higher knowledge retention, and training sessions that take just 20 minutes instead of 90. Corporate leadership programs are another area where VR is transforming training. PwC has used VR-based immersive learning to develop communication, public speaking, and empathy skills in leadership candidates. In a leadership program delivered with Nakheel Properties, participants achieved 44% higher assessment scores after just two days of blended VR training compared to pre-training levels. PwC research found that VR learners complete training up to 4 times faster and are 275% more confident in applying their skills compared to traditional classroom learners. This makes VR a powerful tool for building critical soft skills, boosting self-awareness, and enhancing leadership effectiveness.
Verizon adopted VR simulations to train retail employees on how to handle armed robbery situations. By immersing employees in high-stress scenarios, they gained critical experience in a safe setting, leading to improved situational awareness and confidence.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
Virtual Reality is redefining the landscape of employee training by offering immersive, efficient, and effective alternatives to traditional learning models. As companies prioritise agility, innovation, and human capital development, VR stands out as a transformative tool.
Its ability to deliver standardised, repeatable, and data-rich learning experiences at scale makes it especially appealing for industries with diverse training needs. From safety compliance in manufacturing to soft skills development, VR proves its versatility and value.
Looking ahead, the integration of VR with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and analytics platforms will open new frontiers in adaptive learning, where training programs respond to individual progress in real time. AI-driven insights can identify knowledge gaps, suggest personalised content, and predict future training needs based on performance data.
In a future where the skills gap continues to challenge organisations, and remote work reshapes traditional workplaces, VR will play a central role in preparing employees not just to perform, but to excel. Businesses that embrace immersive training today are investing in the talent, adaptability, and resilience they’ll need tomorrow.
References:
- Allcoat, D., & von Mühlenen, A. (2018). Learning in virtual reality: Effects on performance, emotion and engagement. Research in Learning Technology, Accessed from: https://doi.org/10.25304/rlt.v26.2140
- Huang, H.-M., Rauch, U., & Liaw, S.-S. (2010). Investigating learners’ attitudes toward virtual reality learning environments: Based on a constructivist approach. Computers & Education, Accessed from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2010.05.014
- Johnson-Glenberg, M. C. (2018). Immersive VR and education: Embodied design principles that include gesture and hand controls. Frontiers in Robotics and AI, Accessed from: https://doi.org/10.3389/frobt.2018.00081
- PWC. (2022) What does Virtual Reality and the Metaverse mean for training? Accessed from: How virtual reality is redefining soft skills training: PwC






